전처리 (colab 이용)
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
DATA_PATH = "/content/drive/MyDrive/"
DATA_PATH
SEED = 42
import torch
import numpy as np
# 시드 고정을 위해
import random
import os
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
# titanic 데이터셋 사용
>>> df = pd.read_csv(f"{DATA_PATH}titanic_train.csv")
결측치 미리 채우기
# age 중앙값
>>> df.age = df.age.fillna(df.age.median())
# fare 중앙값
>>> df.fare = df.fare.fillna(df.fare.median())
# cabin 임의의 문자열로 채우기
>>> df.cabin = df.cabin.fillna("UNK")
# embarked 최빈값
>>> df.embarked = df.embarked.fillna(df.embarked.mode()[0])
# 학습에 바로 사용가능한 특성
>>> cols = ["pclass","age","sibsp","parch","fare"]
>>> features = df[cols]
범주형 one-hot encoding
>>> cols = ["gender","embarked"]
>>> enc = OneHotEncoder()
>>> tmp = pd.DataFrame(
>>> enc.fit_transform(df[cols]).toarray(),
>>> columns = enc.get_feature_names_out()
>>> )
# 특성
>>> features = pd.concat([features,tmp],axis=1)
# 정답값
>>> y_train = df["survived"].to_numpy()
스케일링
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
>>> scaler = MinMaxScaler()
>>> x_train = scaler.fit_transform(features)
>>> x_train.shape , y_train.shape
((916, 10), (916,))
재현성 함수 (Reproduction)
- 동일하게 학습되지 않는다 = 예측 결과가 보장되지 않는다 = 재현성이 보장되지 않는다
- 재현성 함수를 돌림으로써 어느정도의 재현성 보장
- 형식이니까 외워라
>>> def reset_seeds(seed):
>>> random.seed(seed)
>>> os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
>>> np.random.seed(seed)
>>> torch.manual_seed(seed)
>>> torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
>>> torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
>>> reset_seeds(SEED)
데이터셋 클래스 만들기
>>> class TitanicDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
>>> def __init__(self,x,y=None):
>>> self.x = x
>>> self.y = y
# 정답 데이터도 같이 들어왔을 때 2차원 형태로 만들어주자
>>> if self.y is not None:
>>> self.y = y.reshape(-1,1)
>>> def __len__(self):
>>> return self.x.shape[0]
>>> def __getitem__(self,idx):
>>> item = {}
>>> item["x"] = torch.Tensor(self.x[idx])
>>> if self.y is not None:
>>> item["y"] = torch.Tensor(self.y[idx])
>>> return item>>> train_dt = TitanicDataset(x_train,y_train)
>>> train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dt,batch_size=2,shuffle = False)
>>> train_dl
<torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader at 0x7ff3faa2b6a0>
>>> data = next(iter(train_dl))
>>> data
{'x': tensor([[0.0000, 0.8873, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0966, 0.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000],
[1.0000, 0.4238, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0157, 0.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
1.0000]]),
'y': tensor([[0.],
[0.]])}


torch.nn.Linear 레이어
- 입력받은 데이터를 선형 변환 해주는 레이어
- fully connected layer 라고도 한다
>>> reset_seeds(SEED)
>>> hidden_layer = torch.nn.Linear(x_train.shape[1],4)
>>> x = hidden_layer(data["x"])
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.2034, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.4339, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
활성화 함수 (Activation function)
- 입력된 데이터의 가중 합을 출력신호로 변환하는 함수
시그모이드 함수 (Sigmoid)
- 0 ~ 1 사이의 값을 가지는 함수

>>> sig = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
>>> sig(x)
tensor([[0.5849, 0.5676, 0.4493, 0.5839],
[0.5127, 0.6320, 0.3932, 0.5992]], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward0>)
탄젠트 함수 (Hyperbolic Tangent)
- -1 ~ 1 사이의 값을 갖는 함수

>>> tanh = torch.nn.Tanh()
>>> tanh(x)
tensor([[ 0.3301, 0.2655, -0.2006, 0.3265],
[ 0.0509, 0.4937, -0.4086, 0.3817]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward0>)
ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)
- 입력이 0 이상이면 입력을 그대로 출력하고, 음수이면 0을 출력
- Dying relu 현상 (노드가 죽는 현상)이 발생하는 문제가 있다
- 비선형성이 추가됨

>>> relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
>>> relu(x)
tensor([[0.3429, 0.2720, 0.0000, 0.3389],
[0.0509, 0.5410, 0.0000, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
Leaky ReLU
- ReLU의 변형된 함수
- Dying ReLU 현상을 해결하기 위해 나온 함수
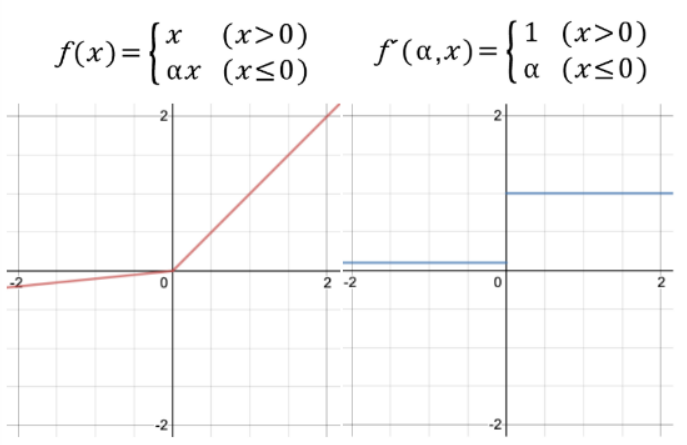
>>> lk_relu = torch.nn.LeakyReLU()
>>> lk_relu(x)
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.0020, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.0043, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<LeakyReluBackward0>)
PReLU (Parametric ReLU)
- Leakly ReLU와 유사하지만 음수 입력에 대한 경사를 학습을 통해 업데이트 함

>>> p_relu = torch.nn.PReLU()
>>> p_relu(x)
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.0508, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.1085, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<PreluKernelBackward0>)
ELU (Exponential Linear Unit)
- 입력이 0 이하일 경우 지수 함수를 이용하여 부드럽게 깎아준다
- exp를 계산하는 비용이 발생함

>>> elu = torch.nn.ELU()
>>> elu(x)
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.1840, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.3520, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<EluBackward0>)
소프트맥스 함수 (Softmax)
- 입력받은 값들을 출력으로 0 ~ 1 사이의 값들로 모두 정규화 하며, 출력값들의 총합은 항상 1이 되는 특성을 가짐
>>> softmax = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1)
>>> softmax(x)
tensor([[0.2852, 0.2657, 0.1651, 0.2840],
[0.2142, 0.3496, 0.1319, 0.3043]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>)
>>> softmax(x).sum(dim=1)
tensor([1.0000, 1.0000], grad_fn=<SumBackward1>)
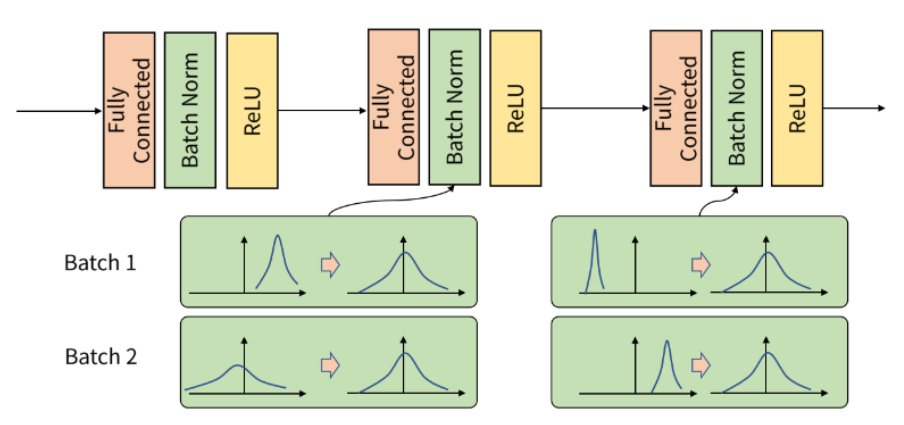
배치 정규화 (Batch Normalization), 노멀리제이션
- 배치 단위로 평균과 분산을 이용해 정규화
- 학습속도 향상
- 경사가 사라지거나 폭발하는 문제를 완화
>>> x
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.2034, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.4339, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
>>> bn = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(x.shape[1])
>>> bn(x)
tensor([[ 0.9998, -0.9997, 0.9996, -0.9950],
[-0.9998, 0.9997, -0.9996, 0.9950]],
grad_fn=<NativeBatchNormBackward0>)
>>> bn(x).mean(), bn(x).var()
(tensor(2.2352e-07, grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>),
tensor(1.1395, grad_fn=<VarBackward0>))
Dropout
- 신경망에서 은닉층의 각 노드에 대해서 (각 노드별) 0 ~ 1 사이 확률로 랜덤하게 0으로 대체
- 빠른 학습 (계산 비용이 작아짐)
- 과대 적합 방지

>>> x
tensor([[ 0.3429, 0.2720, -0.2034, 0.3389],
[ 0.0509, 0.5410, -0.4339, 0.4020]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
>>> dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(0.3)
>>> dropout(x)
tensor([[ 0.0000, 0.3886, -0.2905, 0.4841],
[ 0.0727, 0.7728, -0.6198, 0.5743]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
torch.nn.Sequential
- 입력 텐서가 순차적으로 layer에 통과할 때 사용
>>> seq_layer = torch.nn.Sequential(
>>> torch.nn.Linear(x_train.shape[1],8),
>>> torch.nn.ReLU(),
>>> torch.nn.Linear(8,4),
>>> torch.nn.ReLU(),
>>> torch.nn.Linear(4,1)
>>> )
>>> seq_layer
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=8, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=4, bias=True)
(3): ReLU()
(4): Linear(in_features=4, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
>>> seq_layer(data["x"])
tensor([[0.2635],
[0.2953]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
신경망 모델 만들기
>>> class Net(torch.nn.Module):
>>> def __init__(self,in_features):
>>> super().__init__()
>>> self.seq_layer = torch.nn.Sequential(
>>> torch.nn.Linear(in_features,8),
>>> torch.nn.ReLU(),
>>> torch.nn.Linear(8,4),
>>> torch.nn.ReLU(),
>>> torch.nn.Linear(4,1)
>>> )
>>> def forward(self,x):
>>> return self.seq_layer(x)>>> model = Net(x_train.shape[1])
>>> model(data["x"])
tensor([[-0.2592],
[-0.2592]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
모델 구조 보기
torchsummary
- 첫번째 인수로 모델 객체를 전달
- input_size 파라미터: 피처 갯수를 튜플로 전달
- device 파라미터: "cuda" or "cpu"
>>> import torchsummary
>>> torchsummary.summary(model,input_size=(x_train.shape[1],),device="cpu")
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Linear-1 [-1, 8] 88
ReLU-2 [-1, 8] 0
Linear-3 [-1, 4] 36
ReLU-4 [-1, 4] 0
Linear-5 [-1, 1] 5
================================================================
Total params: 129
Trainable params: 129
Non-trainable params: 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.00
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.00
Params size (MB): 0.00
Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.00
----------------------------------------------------------------
torchinfo
- 첫번째 인수로 모델 객체 전달
- 두번째 인수로 배치 사이즈와 피처 갯수를 튜플로 전달
!pip install torchinfo
>>> import torchinfo
>>> torchinfo.summary(model,(32,x_train.shape[1]) )
==========================================================================================
Layer (type:depth-idx) Output Shape Param #
==========================================================================================
Net [32, 1] --
├─Sequential: 1-1 [32, 1] --
│ └─Linear: 2-1 [32, 8] 88
│ └─ReLU: 2-2 [32, 8] --
│ └─Linear: 2-3 [32, 4] 36
│ └─ReLU: 2-4 [32, 4] --
│ └─Linear: 2-5 [32, 1] 5
==========================================================================================
Total params: 129
Trainable params: 129
Non-trainable params: 0
Total mult-adds (M): 0.00
==========================================================================================
Input size (MB): 0.00
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.00
Params size (MB): 0.00
Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.01
==========================================================================================